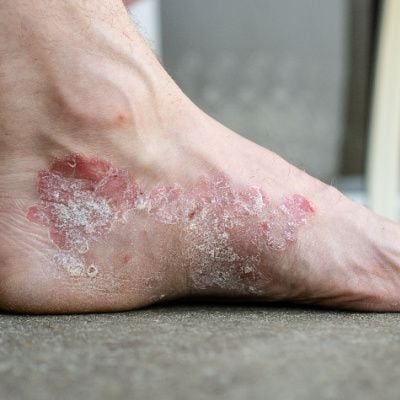
 Foot psoriasis is a dermatological condition that can significantly impact an individual's quality of life. Psoriasis, in general, is an autoimmune disorder characterized by the rapid buildup of skin cells, leading to the formation of scales and red patches. When this condition affects the feet, it presents unique challenges due to the constant pressure and friction these areas endure. In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the intricacies of foot psoriasis, exploring its causes, symptoms, treatment options, and practical tips for managing this condition effectively.
Foot psoriasis is a dermatological condition that can significantly impact an individual's quality of life. Psoriasis, in general, is an autoimmune disorder characterized by the rapid buildup of skin cells, leading to the formation of scales and red patches. When this condition affects the feet, it presents unique challenges due to the constant pressure and friction these areas endure. In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the intricacies of foot psoriasis, exploring its causes, symptoms, treatment options, and practical tips for managing this condition effectively.
Understanding Foot Psoriasis
-
Symptoms:
- Foot psoriasis manifests with symptoms such as red or silvery scales, itching, burning sensations, and dry, cracked skin. In severe cases, psoriasis can also affect the nails, causing discoloration and pitting.
-
Common Areas Affected:
- Psoriasis can affect various foot parts, including the soles, sides, and toenails. The presence of psoriasis on the feet can make standing, walking, and wearing specific shoes uncomfortable.
Causes and Triggers
-
Immune System Dysfunction:
- Psoriasis is primarily an autoimmune disorder where the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy skin cells, causing an accelerated turnover of skin cells.
-
Genetic Predisposition:
- There is a genetic component to psoriasis, and individuals with a family history may be more susceptible.
-
Environmental Factors:
- Triggers such as stress, infections, and certain medications can exacerbate psoriasis symptoms.
Diagnosis and Assessment
-
Visual Examination:
- Dermatologists often diagnose foot psoriasis through a visual examination, considering the appearance and distribution of the lesions.
-
Biopsy:
- Sometimes, a skin biopsy may be performed to confirm the diagnosis and rule out other skin conditions.
Management and Treatment
-
Topical Treatments:
- Corticosteroid creams, ointments, and other topical treatments are commonly prescribed to alleviate inflammation and reduce scaling.
-
Moisturizers:
- Regularly using moisturizers helps keep the skin hydrated, minimizing the dryness associated with psoriasis.
-
Phototherapy:
- Controlled exposure to ultraviolet (UV) light under medical supervision can effectively treat foot psoriasis.
-
Oral Medications:
- In more severe cases, oral medications or biologics may be prescribed to modulate the immune system and reduce symptoms.
-
Foot Care Practices:
- Gentle foot care practices, such as avoiding harsh soaps, trimming nails carefully, and wearing comfortable shoes, can help manage symptoms.
Living with Foot Psoriasis: Practical Tips
-
Choosing Footwear Wisely:
- Opt for shoes that provide ample support and avoid those that may cause friction or pressure on affected areas.
-
Managing Stress:
- Stress management techniques, such as meditation or yoga, can be beneficial in minimizing psoriasis flare-ups.
-
Avoiding Irritants:
- Steer clear of harsh chemicals or irritants that can exacerbate symptoms. This includes certain skincare products or environmental factors.
-
Regular Check-ups:
- Schedule regular check-ups with a dermatologist to monitor the condition and adjust the treatment plan.
Conclusion
Foot psoriasis requires a holistic approach that addresses the condition's physical and emotional aspects. By understanding its triggers, seeking prompt medical attention, and adopting proactive foot care practices, individuals can effectively manage foot psoriasis and improve their overall well-being. This guide aims to empower those navigating foot psoriasis, providing insights to enhance their understanding of the condition and paving the way for a more comfortable and fulfilling life despite its challenges.
Disclaimer:
The information on this website is provided for educational and information purposes only and is not medical advice. Always consult with a licensed medical provider and follow their recommendations regardless of what you read on this website. If you think you are having a medical emergency, dial 911 or go to the nearest emergency room. Links to other third-party websites are provided for your convenience only. If you decide to access any of the third-party websites, you do so entirely at your own risk and subject to the terms of use for those websites. Neither Evanston Foot and Ankle Clinic, nor any contributor to this website, makes any representation, express or implied, regarding the information provided on this website or any information you may access on a third-party website using a link. Use of this website does not establish a doctor-patient relationship. If you would like to request an appointment with a health care provider, please call our office at (847) 864-5010.

